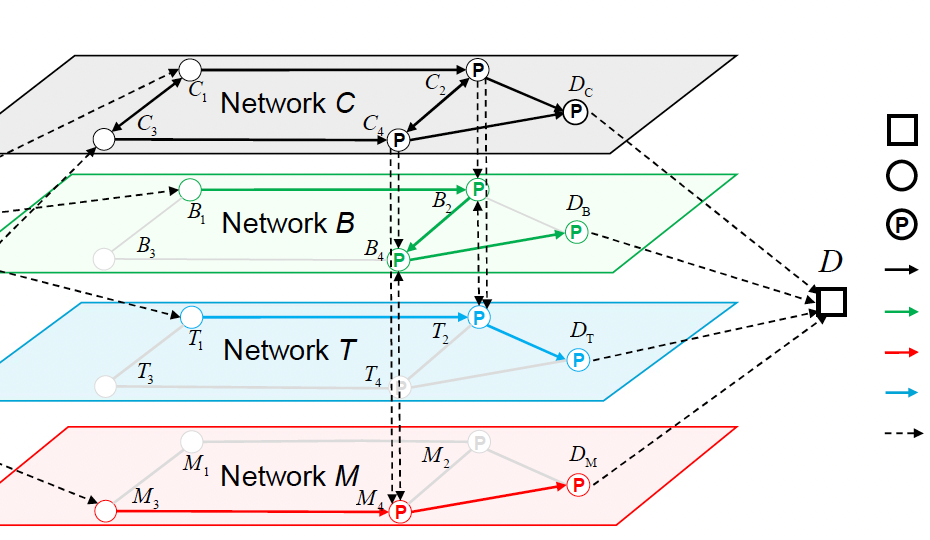
Multi-modal transport is getting more popular due to the emergence of new traffic modes. The increase of modes also adds complexity for the transport researchers. This paper proposes an augmented link-based super-network approach for modeling multi-modal transport networks, addressing the scalability and versatility issues of conventional methods. This approach is used to calculate the user equilibrium for urban transport networks traffic assignment with multiple traffic modes, a difficult problem due to the intractable enumeration of feasible paths between origindestination pairs and restricted transfers between different traffic modes. In the supernetwork representation of multi-modal transport networks, the travel cost of any feasible route between the origin and destination is formulated as the sum of cost functions of the augmented links, thus avoiding the enumeration of feasible paths. Additionally, restrictions on traffic mode transfers can be embedded in the link-based model by excluding infeasible transfer links or adding penalties for undesired transfers. The user equilibrium of the augmented link-based super-network model is formulated as a variational inequality problem, solved using the extra-gradient algorithm. A multimodal transport network is considered in the case study. Simulation results validate the effectiveness of the proposed model, demonstrating its scalability and versatility in addressing complex multi-modal transport networks with diverse traffic modes. We anticipate that our method can serve as an efficient modeling approach for more general and complex multi-modal transport networks, facilitating traffic management and network design..

Author: Dingshan Sun
Publication date: 2025